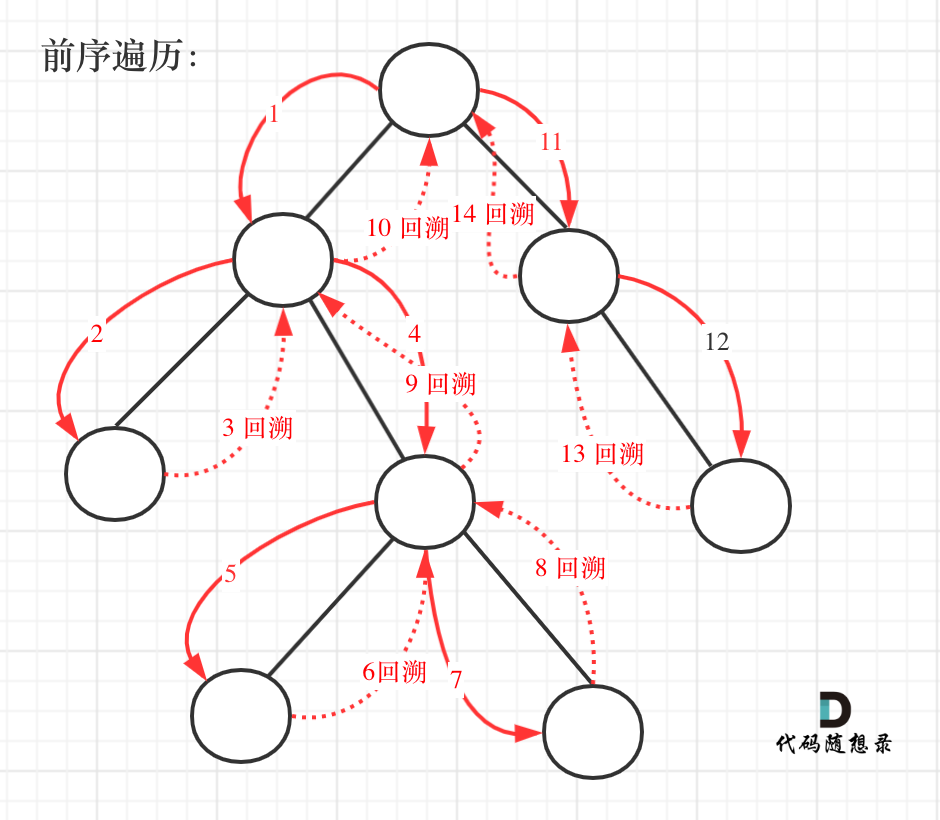
复习 深度优先遍历 前序遍历 递归 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { public List<Integer> preorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList <>(); preorder(root, result); return result; } public void preorder (TreeNode root, List<Integer> result) { if (root == null ) return ; result.add(root.val); preorder(root.left, result); preorder(root.right, result); } }
迭代 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { public List<Integer> preorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList <>(); if (root == null ) return result; Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack <>(); stack.push(root); while (!stack.isEmpty()){ TreeNode node = stack.pop(); result.add(node.val); if (node.right != null ) stack.push(node.right); if (node.left != null ) stack.push(node.left); } return result; } }
统一迭代 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { public List<Integer> preorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList <>(); if (root == null ) return result; Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack <>(); stack.push(root); while (!stack.isEmpty()){ TreeNode node = stack.pop(); if (node != null ){ if (node.right != null ) stack.push(node.right); if (node.left != null ) stack.push(node.left); stack.push(node); stack.push(null ); } else { result.add(stack.pop().val); } } return result; } }
中序遍历 递归 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public List<Integer> inorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList <>(); inorder(root, result); return result; } public void inorder (TreeNode root, List<Integer> result) { if (root == null ) return ; inorder(root.left, result); result.add(root.val); inorder(root.right, result); } }
迭代 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { public List<Integer> inorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList <>(); if (root == null ) return result; Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack <>(); TreeNode cur = root; while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()){ if (cur != null ){ stack.push(cur); cur = cur.left; } else { cur = stack.pop(); result.add(cur.val); cur = cur.right; } } return result; } }
统一迭代 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { public List<Integer> inorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList <>(); if (root == null ) return result; Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack <>(); stack.push(root); while (!stack.isEmpty()){ TreeNode node = stack.pop(); if (node != null ){ if (node.right != null ) stack.push(node.right); stack.push(node); stack.push(null ); if (node.left != null ) stack.push(node.left); } else { result.add(stack.pop().val); } } return result; } }
后序遍历 递归 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution { public List<Integer> postorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList <>(); postorder(root, result); return result; } public void postorder (TreeNode root, List<Integer> result) { if (root == null ) return ; postorder(root.left, result); postorder(root.right, result); result.add(root.val); } }
迭代 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public List<Integer> postorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList <>(); if (root == null ) return result; Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack <>(); stack.push(root); while (!stack.isEmpty()){ TreeNode node = stack.pop(); result.add(node.val); if (node.left != null ) stack.push(node.left); if (node.right != null ) stack.push(node.right); } Collections.reverse(result); return result; } }
统一迭代 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { public List<Integer> postorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList <>(); if (root == null ) return result; Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack <>(); stack.push(root); while (!stack.isEmpty()){ TreeNode node = stack.pop(); if (node != null ){ stack.push(node); stack.push(null ); if (node.right != null ) stack.push(node.right); if (node.left != null ) stack.push(node.left); } else { result.add(stack.pop().val); } } return result; } }
广度优先遍历 DFS 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder (TreeNode root) { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList <>(); dfs(root, 0 , result); return result; } public void dfs (TreeNode root, int depth, List<List<Integer>> result) { if (root == null ) return ; depth++; if (result.size() < depth){ List<Integer> itemList = new ArrayList <>(); result.add(itemList); } result.get(depth - 1 ).add(root.val); dfs(root.left, depth, result); dfs(root.right, depth, result); } }
BFS 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder (TreeNode root) { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList <>(); if (root == null ) return result; Queue<TreeNode> queue = new ArrayDeque <>(); queue.add(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()){ List<Integer> itemList = new ArrayList <>(); int length = queue.size(); while (length-- > 0 ){ TreeNode node = queue.poll(); itemList.add(node.val); if (node.left != null ) queue.add(node.left); if (node.right != null ) queue.add(node.right); } result.add(itemList); } return result; } }
翻转二叉树 递归法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { public TreeNode invertTree (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) return root; swapChildren(root); invertTree(root.left); invertTree(root.right); return root; } public void swapChildren (TreeNode root) { TreeNode node = root.left; root.left = root.right; root.right = node; } }
迭代法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution { public TreeNode invertTree (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) return root; Queue<TreeNode> queue = new ArrayDeque <>(); queue.add(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()){ TreeNode node = queue.poll(); swapChildren(node); if (node.left != null ) queue.add(node.left); if (node.right != null ) queue.add(node.right); } return root; } public void swapChildren (TreeNode root) { TreeNode node = root.left; root.left = root.right; root.right = node; } }
对称二叉树 递归法 在判断左右节点的值时,不能依据两个node是否为null,那样会破坏递归,直接返回值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution { public boolean isSymmetric (TreeNode root) { return compare(root.left, root.right); } public boolean compare (TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { if (left == null && right != null ) return false ; if (left != null && right == null ) return false ; if (left == null && right == null ) return true ; if (left.val != right.val) return false ; boolean compareOutside = compare(left.left, right.right); boolean compareInside = compare(left.right, right.left); return compareOutside && compareInside; } }
迭代法 建立队列时用linkedlist, ArrayDeque不接受null
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { public boolean isSymmetric (TreeNode root) { Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList <>(); queue.offer(root.left); queue.offer(root.right); while (!queue.isEmpty()){ TreeNode left = queue.poll(); TreeNode right = queue.poll(); if (left == null && right == null ) continue ; if (left == null || right == null || left.val != right.val) return false ; queue.offer(left.left); queue.offer(right.right); queue.offer(left.right); queue.offer(right.left); } return true ; } }
二叉树最大深度 递归法 后序遍历
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution { public int maxDepth (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) return 0 ; int left = maxDepth(root.left); int right = maxDepth(root.right); int depth = 1 + Math.max(left, right); return depth; } }
前序遍历
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { int depth = 0 ; public int maxDepth (TreeNode root) { dfs(root, 0 ); return depth; } public void dfs (TreeNode root, int curDepth) { if (root == null ) return ; curDepth++; depth = Math.max(curDepth, depth); dfs(root.left,curDepth); dfs(root.right,curDepth); } }
层序遍历迭代 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public int maxDepth (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) return 0 ; Queue<TreeNode> queue = new ArrayDeque <>(); queue.add(root); int depth = 0 ; while (!queue.isEmpty()){ int length = queue.size(); while (length-- > 0 ){ TreeNode node = queue.poll(); if (node.left != null ) queue.add(node.left); if (node.right != null ) queue.add(node.right); } depth++; } return depth; } }
二叉树最小深度 后序遍历
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { public int minDepth (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) return 0 ; int left = minDepth(root.left); int right = minDepth(root.right); if (root.left == null ){ return 1 + right; } if (root.right == null ){ return 1 + left; } return Math.min(left, right) + 1 ; } }
前序遍历
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { int depth = 0 ; int minDepth = Integer.MAX_VALUE; public int minDepth (TreeNode root) { getDepth(root); return minDepth == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? 0 : minDepth; } public void getDepth (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) return ; depth++; getDepth(root.left); getDepth(root.right); if (root.left == null && root.right== null ) { minDepth = Math.min(minDepth, depth); } depth--; } }
完全二叉树的节点数 后序遍历
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 class Solution { public int countNodes (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) return 0 ; return 1 + countNodes(root.left) + countNodes(root.right); } }
前序遍历 递归
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { int count = 0 ; public int countNodes (TreeNode root) { dfs(root); return count; } public void dfs (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) return ; count++; if (root.left != null ) dfs(root.left); if (root.right != null ) dfs(root.right); } }
检查是不是满完全二叉树, 之后再返回结果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution { public int countNodes (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) return 0 ; int leftDepth = 0 ; int rightDepth = 0 ; TreeNode leftNode = root.left; TreeNode rightNode = root.right; while (leftNode != null ){ leftNode = leftNode.left; leftDepth++; } while (rightNode != null ){ rightNode = rightNode.right; rightDepth++; } if (leftDepth == rightDepth){ return (2 << leftDepth) - 1 ; } return 1 + countNodes(root.left) + countNodes(root.right); } }
110 平衡二叉树 https://leetcode.com/problems/balanced-binary-tree/
判断一个二叉树每个节点左右两个子树的高度差绝对值不超过一
求高度 用后序遍历
在用后序遍历时 求左子树和右子树的高度差值,如果差值小于等于1,返回当前二叉树高度,否则-1;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public boolean isBalanced (TreeNode root) { return getHeight(root) != -1 ; } public int getHeight (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) return 0 ; int leftHeight = getHeight(root.left); if (leftHeight == -1 ) return -1 ; int rightHeight = getHeight(root.right); if (rightHeight == -1 ) return -1 ; if (Math.abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1 ){ return -1 ; } return Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1 ; } }
257 二叉树的所有路径 https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-paths/description/
返回从根节点到叶子节点所有路径 需要前序遍历
此题难点是回溯
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class Solution { public List<String> binaryTreePaths (TreeNode root) { List<String> result = new ArrayList <>(); if (root == null ) return result; List<Integer> paths = new ArrayList <>(); traversal(root, result, paths); return result; } public void traversal (TreeNode root, List<String> result, List<Integer> paths) { paths.add(root.val); if (root.left == null && root.right == null ){ StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder (); for (int i = 0 ; i < paths.size() - 1 ; i++){ sb.append(paths.get(i)).append("->" ); } sb.append(paths.get(paths.size() - 1 )); result.add(sb.toString()); } if (root.left != null ){ traversal(root.left, result, paths); paths.remove(paths.get(paths.size() - 1 )); } if (root.right != null ){ traversal(root.right, result, paths); paths.remove(paths.get(paths.size() - 1 )); } } }
迭代法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class Solution { public List<String> binaryTreePaths (TreeNode root) { List<String> result = new ArrayList <>(); if (root == null ) return result; Stack<Object> stack = new Stack <>(); stack.push(root); stack.push(root.val + "" ); while (!stack.isEmpty()){ String path = (String) stack.pop(); TreeNode node = (TreeNode) stack.pop(); if (node.left == null && node.right == null ){ result.add(path); } if (node.right != null ) { stack.push(node.right); stack.push(path + "->" + node.right.val); } if (node.left != null ){ stack.push(node.left); stack.push(path + "->" + node.left.val); } } return result; } }
404 左叶子之和 计算给定二叉树的所有左叶子之和
递归法 通过后序遍历完成
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { public int sumOfLeftLeaves (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) return 0 ; if (root.left == null && root.right == null ) return 0 ; int leftSum = sumOfLeftLeaves(root.left); int rightSum = sumOfLeftLeaves(root.right); int midValue = 0 ; if (root.left != null && root.left.left == null && root.left.right == null ){ midValue = root.left.val; } return leftSum + rightSum + midValue; } }
迭代法
一个前序迭代,就可以完成
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public int sumOfLeftLeaves (TreeNode root) { Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack <>(); if (root != null ) stack.push(root); if (root == null ) return 0 ; int sum = 0 ; while (!stack.isEmpty()){ TreeNode node = stack.pop(); if (node.left != null && node.left.left == null && node.left.right == null ){ sum += node.left.val; } if (node.right != null ) stack.push(node.right); if (node.left != null ) stack.push(node.left); } return sum; } }